LLM in PyTorch
Building and training a GPT-2 style model in pure PyTorch
Tech Stack
Description
Building an LLM (Large Language Model) has always fascinated me, and Sebastian Raschka’s book Build a Large Language Model was the perfect opportunity to revisit the Transformer architecture in PyTorch. It covers how to convert words into tokens, how to code and use the decoder part of a Transformer (in pure PyTorch, with mathematical formulas) to generate new tokens one by one, how to prepare a dataset for pre-training, how to fine-tune a model on data, and how to implement RLHF (Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback) to make an LLM follow instructions.
Features
- Tokenization: Converting text into tokens with a custom vocabulary
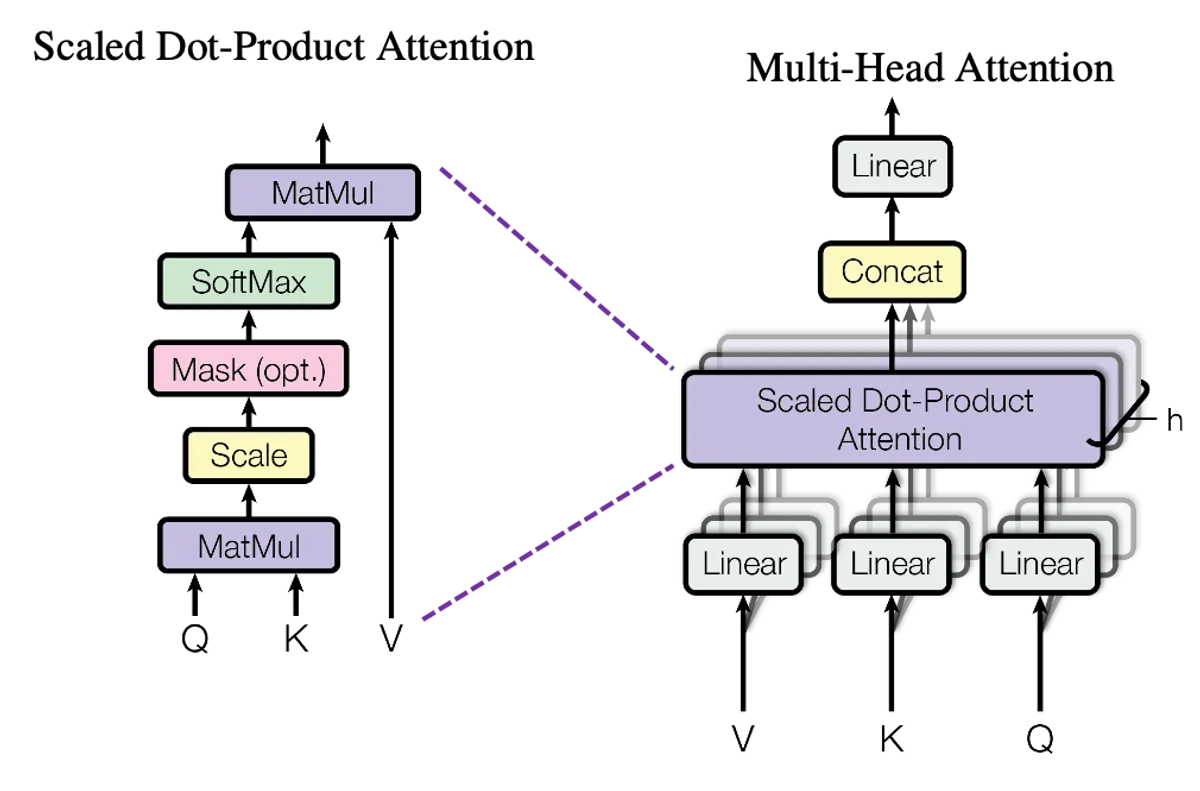
- Transformer Architecture: Complete implementation of the decoder (multi-head attention, layer normalization, feed-forward) in pure PyTorch
- Pre-training: Dataset preparation and model training on next-token prediction
- Fine-tuning: Adapting the pre-trained model to specific tasks
- RLHF: Implementation of Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback for model alignment
Challenges
- Understanding the attention mechanism: Visualizing how the Q, K, V matrices interact and why dividing by √d_k is necessary for numerical stability required several readings and experiments
- Training debugging: Identifying why the loss was stagnating or exploding, tuning hyperparameters (learning rate, batch size, warmup steps) empirically
- Hardware constraints: With an
RTX 5070 Ti, I had to optimizeGPUmemory usage and limit model and batch sizes - Gradient management: Understanding and implementing gradient accumulation to simulate larger batch sizes despite memory limitations
Model Architecture
The implemented model follows OpenAI’s GPT-2 Small architecture:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Parameters | 124M |
| Layers | 12 |
| Embedding dimension | 768 |
| Attention heads | 12 |
| Max context | 1024 tokens |
| Vocabulary | ~50k tokens (BPE) |
This architecture is identical to GPT-3, but at a much smaller scale (GPT-3 has 175 billion parameters compared to 124 million here), making it trainable on consumer hardware.
Results
The model was pre-trained on the Shakespeare corpus (~1 MB of text), giving it a distinctive writing style in Elizabethan English:
- Coherent text generation: The model produces grammatically correct sentences that mimic Shakespearean style, with archaic turns of phrase (“thou”, “hath”, “wherefore”)
- Instruction following: After fine-tuning, the model responds to prompts contextually
- Limitations: The small dataset and model size limits the diversity and depth of responses — the model excels in its narrow domain but doesn’t generalize to other styles or topics